Nervous System And Gut Microbiome - The Progress Of Gut Microbiome Research Related To Brain Disorders Journal Of Neuroinflammation Full Text - Do you go with your gut feeling?
How the gut influences your child's mood and behavior. Multiple sclerosis, or ms, is the most common autoimmune disease of the central nervous system and affects 2.3 million people. The gut microbiota has been shown to contribute to the development of the immune system, and, remarkably, also to the development of the central nervous system (cns). By influencing your stress response. 24 july 2019, robert smith.

The enteric nervous system and gut microbiome.
Stress also has a direct effect on the gut microbiome. The gut communicates with the brain, and the brain communicates with the gut via neurons which line the digestive tract. Think of those nervous butterflies. The brain has a direct effect on the stomach and intestines. Apart from genetic factors, it has been suggested that the gut microbiome may have a part to play in autism spectrum disorders. The lines between the gut and the brain are more blurred than we've ever realized before. Certain bacteria within our gut microbiome can yield specific benefits, both directly and indirectly, to our nervous system. Its main player is the vagal nerve, connecting the internal organs to the brain," Both the nervous system and opioids regulate the composition of the gut microbiome. Actually, this old proverb harbors more truth than you think. While humans are taught that all organ systems are connected and controlled by the central nervous system, the gastrointestinal tract or simply the gut has evolved to have its own nervous system. The nerves and ganglia located in the brain and spinal cord. Briefly, it was shown that the presence.
The human microbiome effects the brain in several different ways. Trauma includes head injuries and concussions, but also inflammatory reactions that injure the central, enteric, and peripheral nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system (stress balance) and the enteric nervous system (gut function). Certain bacteria within our gut microbiome can yield specific benefits, both directly and indirectly, to our nervous system. gut health triad bundle (microbiome gut solution) 95% of your serotonin (the happy hormone) is produced and lives in your microbiome.
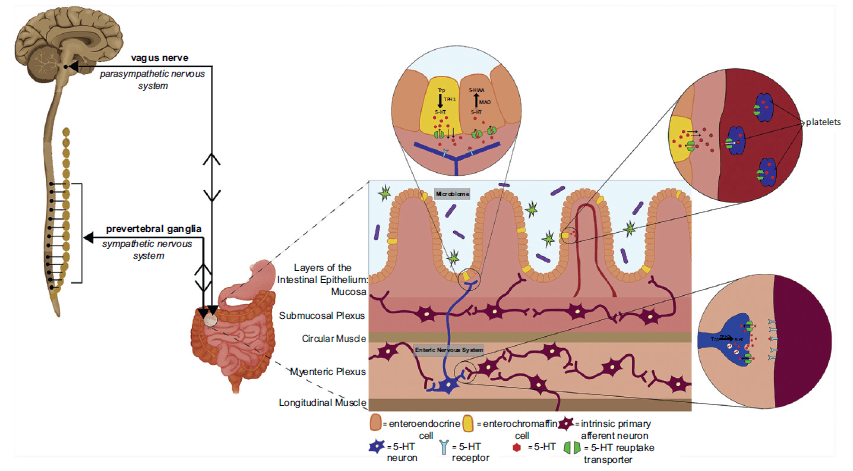
(citing the enteric nervous system's autonomy and apparent infallibility, comedian stephen colbert once christened the gut "the pope of your torso.") at birth, every gut is sterile.
The gut is often referred to as the second brain because the nerves in the gut control digestion independently from the brain. The gut is the organ that hosts the largest concentration of immune cells in your entire body. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. How the gut influences your child's mood and behavior. The exciting developing area is understanding how components of a normal, healthy gut microbiome affect the development of the brain, the integrity. In recent research, it was shown that. Of note, the peripheral nervous system comprises the network of nerves found outside the central nervous system, that of the brain and the spinal cord. While humans are taught that all organ systems are connected and controlled by the central nervous system, the gastrointestinal tract or simply the gut has evolved to have its own nervous system. Do you go with your gut feeling? This connection goes both ways. Think of those nervous butterflies. gut health triad bundle (microbiome gut solution) 95% of your serotonin (the happy hormone) is produced and lives in your microbiome. The gut microbiota has been shown to contribute to the development of the immune system, and, remarkably, also to the development of the central nervous system (cns).
In recent research, it was shown that. Clarke, stilling et al., 2014, for a review of endocrine effects of the gut microbiota), and bacteria found within the. Similar to the brain, the enteric nervous system puts out more than 30 neurotransmitters. 24 july 2019, robert smith. A team of researchers in munich has now succeeded in using violet light to make these migrating t cells visible for the.

Pubmed pubmed central article cas google scholar 9.
A better understanding of its effect could revolutionize our therapy options. Maintenance by neurons of a healthy microbiome could be important in gut physiology and host defense. The influence of gut microbiota on neuroinflammation and motor deficits was demonstrated recently in an animal model of parkinson's disease. The human microbiome effects the brain in several different ways. The gut is the organ that hosts the largest concentration of immune cells in your entire body. Herein, we discuss the biological intersection of neurodevelopment and the microbiome and explore the hypothesis that gut bacteria are integral contributors to development and function of the nervous system and to the balance between mental health and disease. Trauma in the nervous system (brain/spinal cord) can affect the function of the other nervous systems: Future mental health therapies may involve manipulating the bacteria in the gut microbiome. One of the driving motivations for oocs is that the cellular microenvironment for the seeded cells, often as 3d matrices, more closely replicates the organ than a 2d plastic petri dish or well plate. gut bacteria can produce the exact same hormones and neurotransmitters that are used in the nervous system (for a brief review of a few of these substances see part 2 and part 3). Microorganisms dictate our lives, whether we'd like them to or not. This connection goes both ways. Bidirectional communication between the gut microbiome and the brain can occur across numerous physiological channels, including neuroendocrine and neuroimmune pathways and the autonomic nervous system (cryan &
Nervous System And Gut Microbiome - The Progress Of Gut Microbiome Research Related To Brain Disorders Journal Of Neuroinflammation Full Text - Do you go with your gut feeling?. Both the nervous system and opioids regulate the composition of the gut microbiome. But over time, everyone's gut develops a diverse and distinct brew of bacterial species, determined in part by genetics and in part by what bacteria live in and on. It causes an imbalance of good and bad bacteria, as much of the good bacteria is wiped out by the sympathetic nervous system. Colon, bowel and cerebrum flat vector illustration. The nerves and ganglia located in the brain and spinal cord.
Posting Komentar untuk "Nervous System And Gut Microbiome - The Progress Of Gut Microbiome Research Related To Brain Disorders Journal Of Neuroinflammation Full Text - Do you go with your gut feeling?"